Overview
For decades, India labour laws have been known for their complexity, with multiple legislations regulating wages, social security, industrial relations, and workplace safety. To streamline this framework, the Government introduced the new labour laws in India, consolidating 29 central legislations into four labour codes.

These reforms aim to simplify compliance, ensure better worker protection, and provide a uniform system for employers. Businesses, especially private companies, must stay informed about the new labour code, the new wage code, and the pending 4 labour code implementation date to remain compliant with evolving regulations.
Why Were New Labour Laws Introduced?
The earlier system of fragmented laws created duplication, confusion, and compliance burdens. By bringing them under four labour codes, the government seeks to:
- Remove inconsistencies between state and central laws
- Streamline definitions of “wages” and “employees”
- Provide clarity in industrial dispute resolution and Rretrenchment labour law
- Expand social security to cover unorganised, gig, and platform workers
- Ensure workplace safety and welfare standards
The Four Labour Codes at a Glance
| Labour Code | Focus Area | Key Replacements |
|---|---|---|
| Code on Wages, 2019 | Minimum wages, equal pay, bonus, timely payment | Merges Minimum Wages Act, Payment of Wages Act, Payment of Bonus Act, Equal Remuneration Act |
| Industrial Relations Code, 2020 | Trade unions, strikes, layoffs, retrenchment | Replaces Industrial Disputes Act, Trade Unions Act, Industrial Employment Act |
| Code on Social Security, 2020 | EPF, ESI, maternity, gig workers, welfare | Combines multiple social security laws, ESI & health |
| Occupational Safety, Health & Working Conditions Code, 2020 | Workplace safety, health, welfare facilities | Brings together Factories Act and other safety laws. |
4 Labour Code Implementation Date
Although Parliament has passed the four codes, their implementation date has not been uniformly notified.
- Expected to be rolled out in phases.
- Draft rules have already been prepared by the Central Government.
- Several states and union territories have pre-published their draft rules.
- Once harmonised, the government will announce the 4 labour code implementation date
Businesses should proactively align policies and systems with the new labour laws in India to avoid last-minute compliance challenges.
Retrenchment Labour Law under the New Regime
Retrenchment labour law has always been a critical area of Indian employment law. Under the old framework, the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947 required:
- One month’s notice or wages in lieu of notice
- Compensation equal to 15 days’ average pay for every completed year of service
- Prior government approval for layoffs and closures in larger establishments
- “Last in, first out” principle while reducing workforce
These safeguards continue until the Industrial Relations Code is fully operational. Private companies must ensure they follow proper procedures while implementing retrenchments or layoffs to avoid legal disputes
Labour Laws in India for Private Companies
For private companies, adapting to the new labour laws in India means:
- Updating HR policies, payroll systems, and employment contracts in line with the new wage code
- Tracking state-specific notifications since labour is a concurrent subject
- Preparing for expanded obligations under social security laws
- Ensuring workplace safety under the Occupational Safety Code
- Managing retrenchment and downsizing legally and fairly
Compliance is not just about avoiding penalties;
it strengthens employee trust and improves industrial relations.
Key Changes under the New Wage Code
The new wage code introduces uniformity in wage calculations and expands coverage to more categories of employees.
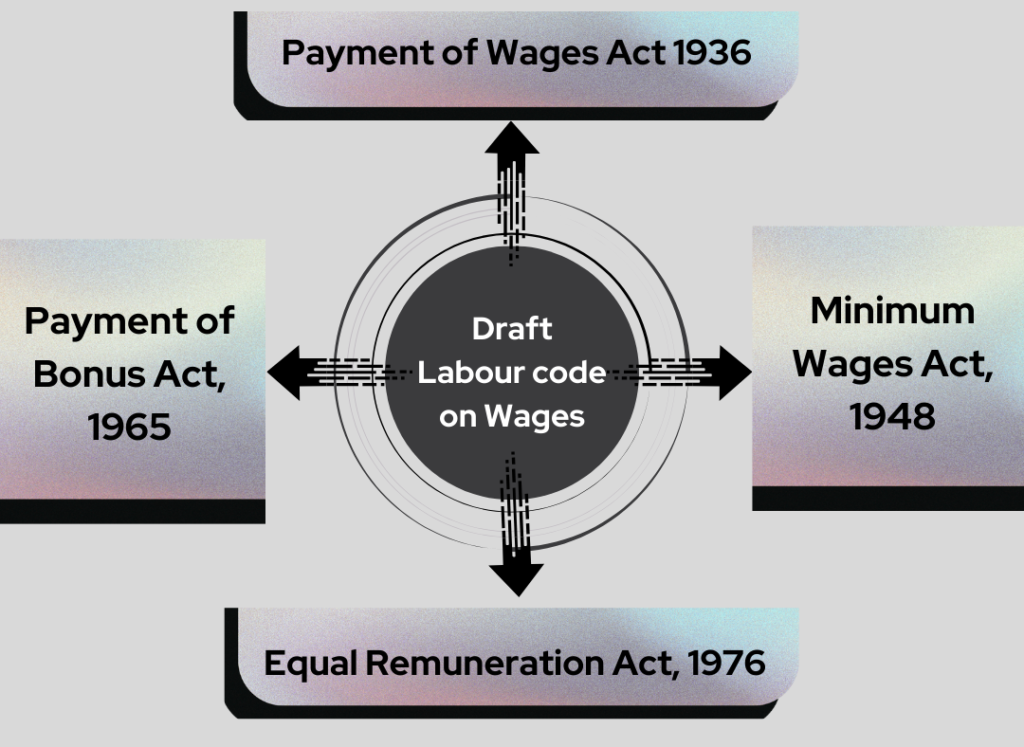
Highlights include:
- Coverage for workers previously excluded under old legislations
- A national floor wage that sets a minimum standard across all states
- Rules for timely payment of wages to prevent delays
- Simplified compliance by merging four wage-related laws
Benefits & Concerns of the New Labour Code
Benefits
- Easier compliance with unified definitions and simplified returns
- Broader coverage for workers including gig and unorganised sectors
- Better wage protection and timely payments
- Modernised workplace safety and welfare norms
Concerns
- Implementation delays create uncertainty
- Critics argue it may ease retrenchment for employers, raising worker concerns
- Variation in state rules may affect uniformity
- Smaller companies may face adjustment challenges during the transition
What Employers Should Do Now
Highlights include:
- Conduct a compliance audit of current labour law practices
- Identify gaps compared to the requirements of the new labour codes
- Revise employment contracts and HR policies
- Stay updated on the official 4 labour code implementation date
- Train HR and legal teams on new compliance standards
- Seek professional advisory for smooth transition
Conclusion of Labour Laws and labour codes
The introduction of new labour laws in India is a landmark reform aimed at simplifying compliance and expanding worker protection. While the official implementation date of the 4 labour codes is awaited, employers—especially private companies—must prepare for the transition.
Understanding the new wage code, retrenchment labour law, and other aspects of the new labour code will help businesses stay compliant and future-ready under the evolving landscape of India labour laws.
